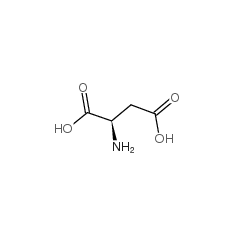
CAS No.: 56-84-8 Formula: C4H7NO4
Weight: 133.10300
Synonyms: L-Asparticacid; asparagic acid; 1-amino-1,2-carboxyethane; L-Aspartic acid;
Aspartic acid (abbreviated as Asp or D; encoded by the codons [GAU and GAC]), also known as aspartate, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH+ 3 form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain CH2COOH. Under physiological conditions in proteins the sidechain usually occurs as the negatively charged aspartate form, −COO−. It is semi-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it from oxaloacetate. In proteins aspartate sidechains are often hydrogen bonded, often as asx turns or asx motifs, which often occur at the N-termini of alpha helices. Asp's L-isomer is one of the 23 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the building blocks of proteins. Asp (and glutamic acid) is classified as acidic, with a pKa of 3.9, however in a peptide this is highly dependent on the local environment (as with all amino acids), and could be as high as 14. Asp is pervasive in biosynthesis. L-aspartic acid is one of the two main ingredients of the artificial sweetener aspartame, along with L-phenylalanine.